更新时间:2022-09-23 17:10:50 来源:动力节点 浏览1449次
学习Java中的反射其实不难,反射是一种 API,用于在运行时检查或修改方法、类和接口的行为。反射所需的类在java.lang.reflect包下提供,这对于理解反射至关重要。所以我们用视觉辅助来说明这个包,以便更好地理解如下:
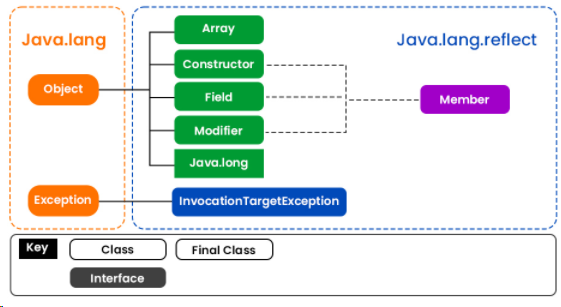
反射可用于获取有关类、构造函数和方法的信息,如下表所示:
班级 getClass() 方法用于获取对象所属的类的名称。
构造函数getConstructors() 方法用于获取对象所属类的公共构造函数。
方法getMethods() 方法用于获取对象所属类的公共方法。
如果我们知道它的名称和参数类型,我们可以通过反射调用方法。为此,我们使用如下所述的两种方法,然后继续进行如下操作:
getDeclaredMethod()
调用()
方法一: getDeclaredMethod (): 创建要调用的方法的对象。
语法:此方法的语法
Class.getDeclaredMethod(名称,参数类型)
参数:
方法二: invoke():它在运行时调用类的方法我们使用下面的方法。
句法:
Method.invoke(对象,参数)
提示:如果类的方法不接受任何参数,则将 null 作为参数传递。
注意:通过反射,我们可以借助类对象访问类的私有变量和方法,并使用上面讨论的对象调用方法。为此,我们使用以下两种方法。
方法三: Class.getDeclaredField(FieldName):用于获取私有字段。返回指定字段名称的 Field 类型的对象。
方法 4: Field.setAccessible(true): 允许访问该字段,而不考虑与该字段一起使用的访问修饰符。
从反射 API 得出的重要观察结果
可扩展性特性:应用程序可以通过使用它们的完全限定名称创建可扩展性对象的实例来使用外部的、用户定义的类。
调试和测试工具:调试器使用反射属性来检查类的私有成员。
性能开销:反射操作的性能比非反射操作慢,在性能敏感的应用程序中频繁调用的代码部分应避免使用。
内部暴露:反射代码破坏了抽象,因此可能会随着平台的升级而改变行为。
例子
// Java Program to demonstrate the Use of Reflection
// Importing required classes
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
// Class 1
// Of Whose object is to be created
class Test {
// creating a private field
private String s;
// Constructor of this class
// Constructor 1
// Public constructor
public Test() { s = "GeeksforGeeks"; }
// Constructor 2
// no arguments
public void method1()
{
System.out.println("The string is " + s);
}
// Constructor 3
// int as argument
public void method2(int n)
{
System.out.println("The number is " + n);
}
// Constructor 4
// Private method
private void method3()
{
System.out.println("Private method invoked");
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
// Creating object whose property is to be checked
// Creating an object of class 1 inside main()
// method
Test obj = new Test();
// Creating class object from the object using
// getClass() method
Class cls = obj.getClass();
// Printing the name of class
// using getName() method
System.out.println("The name of class is "
+ cls.getName());
// Getting the constructor of the class through the
// object of the class
Constructor constructor = cls.getConstructor();
// Printing the name of constructor
// using getName() method
System.out.println("The name of constructor is "
+ constructor.getName());
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"The public methods of class are : ");
// Getting methods of the class through the object
// of the class by using getMethods
Method[] methods = cls.getMethods();
// Printing method names
for (Method method : methods)
System.out.println(method.getName());
// Creates object of desired method by
// providing the method name and parameter class as
// arguments to the getDeclaredMethod() method
Method methodcall1
= cls.getDeclaredMethod("method2", int.class);
// Invoking the method at runtime
methodcall1.invoke(obj, 19);
// Creates object of the desired field by
// providing the name of field as argument to the
// getDeclaredField() method
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("s");
// Allows the object to access the field
// irrespective of the access specifier used with
// the field
field.setAccessible(true);
// Takes object and the new value to be assigned
// to the field as arguments
field.set(obj, "JAVA");
// Creates object of desired method by providing the
// method name as argument to the
// getDeclaredMethod()
Method methodcall2
= cls.getDeclaredMethod("method1");
// Invokes the method at runtime
methodcall2.invoke(obj);
// Creates object of the desired method by providing
// the name of method as argument to the
// getDeclaredMethod() method
Method methodcall3
= cls.getDeclaredMethod("method3");
// Allows the object to access the method
// irrespective of the access specifier used with
// the method
methodcall3.setAccessible(true);
// Invoking the method at runtime
methodcall3.invoke(obj);
}
}
输出:

以上就是动力节点小编介绍的"Java反射学习,要点你抓好了吗",希望对大家有帮助,如有疑问,请在线咨询,有专业老师随时为您务。
 Java实验班
Java实验班
0基础 0学费 15天面授
 Java就业班
Java就业班
有基础 直达就业
 Java夜校直播班
Java夜校直播班
业余时间 高薪转行
 Java在职加薪班
Java在职加薪班
工作1~3年,加薪神器
 Java架构师班
Java架构师班
工作3~5年,晋升架构
提交申请后,顾问老师会电话与您沟通安排学习